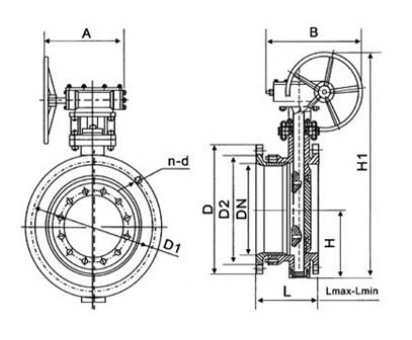
External dimension, flange dimension and bolt hole dimension of telescopic butterfly valve
Expansion butterfly valve, as a component used to realize on-off and flow control of pipeline system, has been widely used in many fields such as petroleum, chemical industry, metallurgy, hydropower and so on. The butterfly plate of the telescopic butterfly valve is installed in the diameter direction of the pipeline. In the cylindrical channel of the butterfly valve body, the disc butterfly plate rotates around the axis, and the rotation angle is between 0 ~90 and when the rotation angle is between 0 and 90 the self-operated valve is fully open. This valve is generally installed horizontally.
Structural characteristics of telescopic butterfly valve:
The expansion butterfly valve has the characteristics of simple structure, small volume, light weight, low material consumption, small installation size, switching rapidly, 90 degree reciprocating rotation, small driving moment, etc. It is used to cut off, connect and regulate the medium in the pipeline, and has good fluid control characteristics and sealing performance. When the expansion butterfly valve is in full open position, the thickness of the expansion butterfly valve is the only resistance when the medium flows through the valve body, so the pressure drop generated by the valve is very small, so it has better flow control characteristics. The expansion butterfly valve has elastic seal and metal seal. Elastic sealing valve, sealing ring can be embedded in the valve body or attached to the butterfly plate.
Metal-sealed telescopic butterfly valves generally have longer life than elastic-sealed valves, but it is difficult to achieve complete sealing. Metal seal can adapt to higher working temperature, while elastic seal has the defect of temperature limitation. If the expansion butterfly valve is required to be used as flow control, the main thing is to correctly select the size and type of the valve. The structure principle of telescopic butterfly valve is especially suitable for making large caliber valves. Telescopic butterfly valves are not only widely used in petroleum, gas, chemical industry, water treatment and other general industries, but also used in the cooling water system of thermal power plants.
The commonly used telescopic butterfly valves are butterfly valves with pair clamps, manual flanged telescopic butterfly valves and butt welded butterfly valves. The butterfly valve is connected between two pipeline flanges by double-head bolts; the flanged butterfly valve is connected with flanges on the valve, and the flanges on both ends of the valve are connected with pipeline flanges by bolts; the two ends of butterfly valve are welded with pipeline flanges. The streamlined design of butterfly plate can reduce the loss of fluid resistance, so it is an energy-saving product. The valve stem is a through-rod structure. After quenching and tempering treatment, it has good comprehensive mechanical properties, corrosion resistance and scratch resistance. When the butterfly valve is opened and closed, the stem is only rotated but not lifted. The filler of the stem is not easy to destroy and the seal is reliable. Fixed with the butterfly plate cone pin, the extension end is anti-washout design, so as to avoid the valve stem collapse when the connection between the stem and the butterfly plate accidentally breaks.
1. Small and light, easy to disassemble and repair, and can be installed at any position.
2. The structure is simple and compact, the operation torque is small, and the 90-degree rotation opens quickly.
3. Flow characteristic tends to straight line and has good regulation performance.
4. The connection between butterfly plate and valve stem adopts pinless structure, which overcomes possible internal leakage points.
5. Seals can be replaced, and the seals are reliable to achieve bidirectional seals.
6. The butterfly plate can be sprayed with coating according to user's requirements, such as nylon or PTFE.
7. The valve can be designed as flange connection and clamp connection.
8. The driving mode can be manual, electric or pneumatic.
Standard for use of telescopic butterfly valves
Design criteria: GB/T12238-1989
Flange connection dimensions: GB/T9113.1-2000; GB/T9113.2-2000
GB/T9115.1-2000; GB/T9115.2-2000
Pressure test: GB/T13927-1992; JB/T9092-1999
Working principle of telescopic butterfly valve
Expansion butterfly valve is a kind of valve which uses circular butterfly plate as opening and closing parts and rotates with the stem to open, close and adjust the fluid passage. The butterfly plate of the telescopic butterfly valve is installed in the diameter direction of the pipeline. In the cylindrical passage of the telescopic butterfly valve body, the disc butterfly plate rotates around the axis, and the rotation angle is between 0 ~90. When the rotation angle is between 0 ~90, the valve is fully open.
Structural diagram of telescopic butterfly valve
Main technical parameters of telescopic butterfly valve:
|
Nominal diameter |
DN(mm) |
50~2000 |
||
|
Nominal pressure |
PN(MPa) |
0.6 |
1.0 |
1.6 |
|
Test pressure |
strength test |
0.9 |
1.5 |
2.4 |
|
Sealing test |
0.66 |
1.1 |
1.76 |
|
|
Gas seal test |
0.6 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
|
|
Applicable temperature |
≤80℃ |
|||
|
Applicable medium |
Air, water, steam, gas, oil, etc. |
|||
|
Driving form |
Manual, worm and worm gear transmission, pneumatic transmission, electric transmission. |
|||
Material of main parts of telescopic butterfly valve
|
Part name |
Material Science |
|
valve body |
Cast iron, cast steel, stainless steel, chromium-molybdenum steel, alloy steel |
|
Disc |
Cast steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, chromium-molybdenum steel |
|
Seal ring |
Rubber, PTFE, Polylactone, Stainless Steel |
|
Stem |
2Cr13, stainless steel, chromium-molybdenum steel |
|
Telescopic tube |
Cast iron, cast steel, stainless steel, chromium-molybdenum steel |
|
filler |
Flexible graphite |
External dimension, flange dimension and bolt hole dimension of telescopic butterfly valve
|
Nominal path |
Shape size (reference value) |
Flange size and bolt hole size (standard value) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
H |
H1 |
Design Maximum Length |
Design Minimum Length |
Design Length |
A |
B |
0.6MPa |
1.0MPa |
1.6MPa |
||||||||||
|
millimeter |
D |
D1 |
D2 |
n-d |
D |
D1 |
D2 |
n-d |
D |
D1 |
D2 |
n-d |
|||||||
|
50 |
80 |
309 |
186 |
156 |
171 |
180 |
200 |
140 |
110 |
88 |
4-14 |
165 |
125 |
99 |
4-18 |
165 |
125 |
99 |
4-18 |
|
65 |
95 |
337 |
190 |
160 |
175 |
180 |
200 |
160 |
130 |
108 |
4-14 |
185 |
145 |
118 |
4-18 |
185 |
145 |
118 |
4-18 |
|
80 |
98 |
347 |
198 |
166 |
182 |
180 |
200 |
190 |
150 |
124 |
4-18 |
200 |
160 |
132 |
8-18 |
200 |
160 |
132 |
8-18 |
|
100 |
114 |
373 |
228 |
188 |
208 |
180 |
200 |
210 |
170 |
144 |
4-18 |
220 |
180 |
156 |
8-18 |
220 |
180 |
156 |
8-18 |
|
125 |
128 |
405 |
240 |
201 |
220 |
180 |
200 |
240 |
200 |
174 |
8-18 |
250 |
210 |
184 |
8-18 |
250 |
|
|
|



 021-59141010
021-59141010